2.1 将维度设置为二维的结果 各参照确定标准:以对应症候群的症状为阳性,赋值为1;以其他症候群症状为阴性,赋值为0,将其作为个体数值与其他病例数据放在一起进行分析得到参照数值。对于参照数据,计算得其二维坐标值(
图1):点1肾虚髓亏(-1.07,0.01),点2阳虚寒凝(1.06,-2.63),点3瘀血阻滞(1.34,1.02)。
膝骨关节炎参照较为分散,表明3个症候群各临床症候有一定差别。此时考虑3个症候群粗分规定:维度一数值小于0者为肾虚髓亏型;维度一大于0,维度二大于0者为瘀血阻滞型,维度一大于0,维度二小于0者为阳虚寒凝型。将其他患者数据计算得的坐标值描入图中,得到患者个体分类坐标图(图2)。

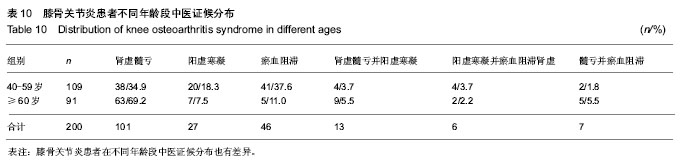
根据对应分析粗分标准,肾虚髓亏型103例占51.05%,阳虚寒凝41例占20.05%,瘀血阻滞56例占28%,从维度图2中显示多数个体值能够分别集中在3个症候群参照周围,但也有一部分样本数据分散在外围,提示还存在其他兼夹证型(
表1)。
 2.2 对应分析粗分与两步聚类法比较
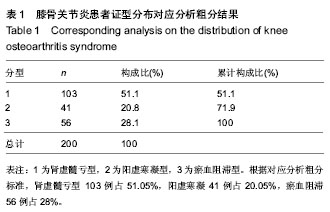
2.2 对应分析粗分与两步聚类法比较 两者分型相同为肾虚髓亏型69例占34.5%,阳虚寒凝36例占18%,瘀血阻滞39例占19.5%,当聚类分析对样本进行聚类时,将靠近不同类的边界部分的样本简单地通过界值加以区分。靠近边界的
样本可能单独为一类,此时结合《中医病证诊断疗效标准》对其中个体样本作中医症候辨证进行重新分类,找出《中医病证诊断疗效标准》症候群之外的证型,聚类分析无法完成;在应用对应分析后,显示多数个体值能够分别集中在3个症候群参照周围,但也有一部分样本数据分散在外围,提示还存在其他兼夹证型,因此本课题尝试采用对应分析研究;对应分析粗分与两步聚类法比较结果见
表2。
配对卡方值为35.575,
P < 0.01,两法判断有差异,因无相关研究故以参照数据坐标为圆心,由小到大尝试其半径大小,结合《中医病证诊断疗效标准》分型标准确定症候群范围。
2.3 确定3个症候群范围 尝试半径有0.5,1.0和1.5,规定半径内的个体值归属于相应症候群。结果如下:
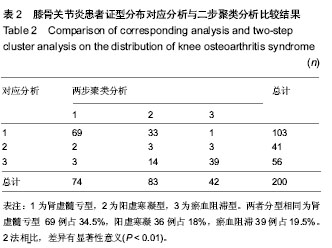
半径0.5:自动分析结果肾虚髓亏型85例占42.05%,阳虚寒凝型7例占3.5%,瘀血阻滞型28例占14%,未知证型80例占40%。从未知证型中随机抽样44例,经本专业专家结合中医理论确定,肾虚髓亏型9例,阳虚寒凝型17例,瘀血阻滞型10例,兼夹型8例,其中肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型7例,阳虚寒凝合并瘀血阻滞型1例。肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型包括症状为隐痛、骨节疼痛、刺痛、固定痛、冷痛、俯仰转侧不利、关节畸形、肿胀积液、头晕、恶风畏寒、腰膝酸软、喜暖怕冷、遇寒痛增、得热稍减、烦闷不安、少气懒言、失眠多梦、闭经、舌质淡红、舌苔薄白、脉弦细;阳虚寒凝合并瘀血阻滞型包括症状主要为刺痛、固定痛、腰膝酸软、活动不利、肿胀积液、四肢乏力、恶风畏寒、面色苍白、喜暖怕冷、遇寒痛增、得热稍减、闭经、舌质淡暗、舌苔白、脉沉涩。说明尝试0.5规定半径内的个体值归属于相应症候群显然和传统中医理论辨证分型误差太大(
表3)。
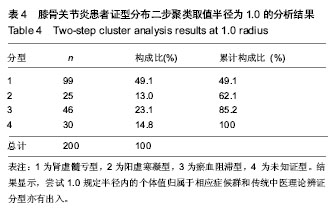
 半径1.0
半径1.0:肾虚髓亏型 99例占49.05%,阳虚寒凝25例占12.05% ,瘀血阻滞46例占23%,未知证型30例占15%,在未知证型中,经结合中医理论及咨询本专业专家确定,肾虚髓亏型2例,阳虚寒凝型2例,兼夹型26例,其中肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型13例,阳虚寒凝合并淤血阻滞型6例,肾虚髓亏合并瘀血阻滞型7例。肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型包括症状为隐痛、骨节疼痛、刺痛、固定痛、冷痛、俯仰转侧不利、关节畸形、肿胀积液、头晕、恶风畏寒、腰膝酸软、喜暖怕冷、遇寒痛增、得热稍减、烦闷不安、少气懒言、失眠多梦、闭经、舌质淡红、舌苔薄白、脉弦细;阳虚寒凝合并瘀血阻滞型包括症状主要为刺痛、固定痛、腰膝酸软、活动不利、肿胀积液、四肢乏力、恶风畏寒、面色苍白、喜暖怕冷、遇寒痛增、得热稍减、闭经、舌质淡暗、舌苔白、脉沉涩。肾虚髓亏合并瘀血阻滞型包括隐痛、骨节疼痛、刺痛、固定痛、关节畸形、耳鸣、四肢乏力、烦闷不安、神疲懒动、少气懒言、闭经、活动不利、肿胀积液、痿弱无力、头晕、舌质淡暗、舌苔白、脉弦细弱或脉沉涩。上述结果显示,尝试1.0规定半径内的个体值归属于相应症候群和传统中医理论辨证分型亦有出入,此分型科学合理性有待商槯(
表4)。
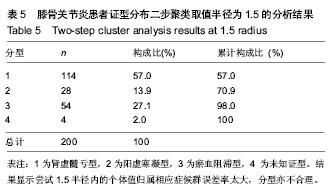
 半径1.5
半径1.5:肾虚髓亏型114例占57%,阳虚寒凝28例占14%,瘀血阻滞54例占27%,未知证型4例占2%。此4例未知证型分别为调查病例肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型3例,症状为隐痛、骨节疼痛、刺痛、固定痛、冷痛、俯仰转侧不利、关节畸形、肿胀积液、头晕、恶风畏寒、腰膝酸软、喜暖怕冷、遇寒痛增、得热稍减、烦闷不安、少气懒言、失眠多梦、闭经、舌质淡红、舌苔薄白、脉弦细;肾虚髓亏合并瘀血阻滞型1例;包括隐痛、骨节疼痛、刺痛、固定痛、关节畸形、耳鸣、四肢乏力、烦闷不安、神疲懒动、少气懒言、闭经、活动不利、肿胀积液、痿弱无力、头晕、舌质淡暗、舌苔白、脉沉涩。此外经2名本专业专家诊断,有13例肾虚髓亏型归类错误,其中10例应归属于肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型,3例应归属于肾虚髓亏合并瘀血阻滞型;1例阳虚寒凝应归属于阳虚寒凝并瘀血阻滞型;8例瘀血阻滞型其中3例应归属于肾虚髓亏并瘀血阻滞型,5例应归属于阳虚寒凝并瘀血阻滞型。上述结果显示尝试1.5半径内的个体值归属相应症候群误差率太大,分型亦不合理(表5)。
根据尝试半径0.5,1.0和1.5内的个体值归属于相应症候群结果,结合《中医病证诊断疗效标准》诊断标准,证型归类均不完全准确。其中0.5误差最大,1.5次之,1.0 误差最小。故细化采取尝试半径1.0-1.5之间数值1.1,1.2,1.3和1.4规定半径内的个体值归属于相应症候群。结果如下:
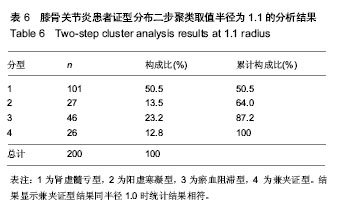
半径1.1:肾虚髓亏型101例占50.5%,阳虚寒凝27例占13.5%,瘀血阻滞46例占23%,兼夹型26例占13%。经2名本专业专家确诊为肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型13例占6.5%,阳虚寒凝合并瘀血阻滞型6例占3%,肾虚髓亏合并瘀血阻滞型7例占3.5%。兼夹证型结果同半径1.0时统计结果相符(表6)。
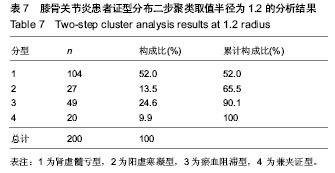
 半径1.2
半径1.2:肾虚髓亏型104例占52%,阳虚寒凝27例占13.5%,瘀血阻滞49例占24.5%,兼夹型20例占10%,其中肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型11例,阳虚寒凝合并瘀血阻滞型3例肾虚髓亏合并瘀血阻滞型6例;经2名本专业专家确诊,与半径1.1相比较增加的3个肾虚髓亏型为肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型2例,肾虚髓亏合并瘀血阻滞型1例,增加3个瘀血阻滞型为3例阳虚寒凝合并瘀血阻滞型(
表7)。
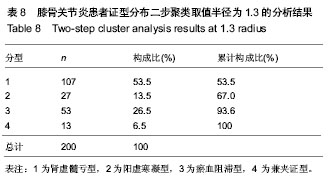
 半径1.3
半径1.3:肾虚髓亏型107例占53.5%;阳虚寒凝27例占13.5%;瘀血阻滞53例占26.5%,兼夹型13例占6.5%;其中肾虚髓亏并阳虚寒凝型10例肾虚髓亏并瘀血阻滞型3例,经2名本专业专家诊断,其中6例肾虚髓亏型诊断为肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型3例,肾虚髓亏合并瘀血阻滞型3例;7例瘀血阻滞型为6例阳虚寒凝合并瘀血阻滞型,肾虚髓亏合并瘀血阻滞型1例(
表8)。
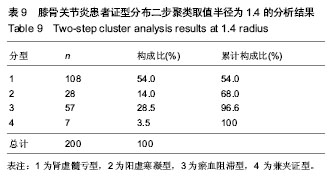
 半径1.4
半径1.4:肾虚髓亏型 108例占54%,阳虚寒凝28例占14%,瘀血阻滞57例占28.5%,兼夹性肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型7例占3.5%。经2名本专业专家诊断,其中 7例肾虚髓亏型确诊为肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝型5例,肾虚髓亏并瘀血阻滞型2例;1例阳虚寒凝型确诊为肾虚髓亏合并阳虚寒凝1型;11例瘀血阻滞型确诊为肾虚髓亏合并瘀血阻滞型5例,阳虚寒凝并瘀血阻滞型6例(
表9)。
 2.4 本次调查对象证型分布特征
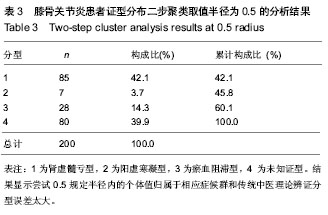
2.4 本次调查对象证型分布特征 200例患者中40-59岁共109例,其中肾虚髓亏38例34.9%,阳虚寒凝20例18.3%,瘀血阻滞41例37.6%,肾虚髓亏并阳虚寒凝4例3.7%,阳虚寒凝并瘀血阻滞4例3.7%,肾虚髓亏并瘀血阻滞2例1.8%。≥ 60岁共91例,其中肾虚髓亏63例69.2%,阳虚寒凝7例7.5%,瘀血阻滞5例11.0%,肾虚髓亏并阳虚寒凝9例9.9%,阳虚寒凝并瘀血阻滞2例2.2%,肾虚髓亏并瘀血阻滞5例5.5%(
表10)。